Night Vision Goggles Ain’t Actually That Complicated
Have you ever watched a spy movie or TV show? If so, you’ve likely seen a scene where a spy uses special glasses to navigate in total darkness. These amazing tools, called night vision goggles, make it possible to see what’s hidden in the shadows. But how do they actually work? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of night vision technology!
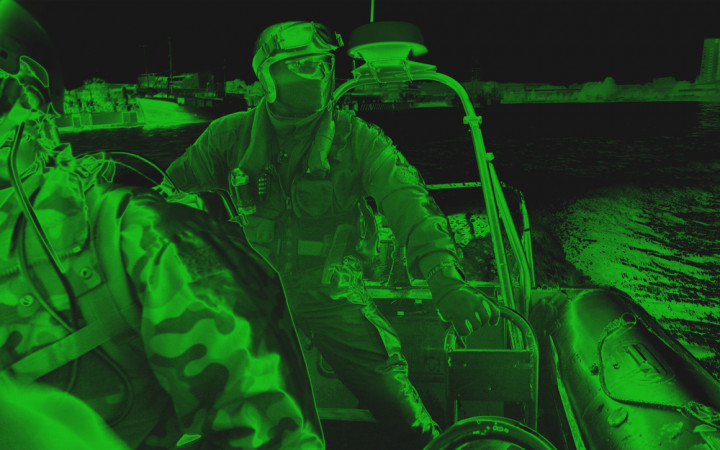

Do Night Vision Goggles Really Work?
If you’re wondering whether night vision goggles are as effective as they seem, the answer is a resounding yes! These devices work incredibly well, even in conditions where the human eye struggles to see anything. On a pitch-black, moonless night, high-quality night vision goggles can help people see objects clearly at distances over 200 yards.
To understand how this is possible, it’s important to first learn a little about light. Did you know that not all light is visible to the human eye? It’s true! The light we see is called visible light, and it’s just a small slice of the electromagnetic spectrum. Beyond visible light, there are other types of light, such as infrared and ultraviolet, that are invisible to the naked eye but play a key role in how night vision goggles work.
The Technology Behind Night Vision Goggles
Night vision goggles function using one of two types of technology: image enhancement or thermal imaging. Let’s take a closer look at both of these amazing systems.
Image Enhancement
Image enhancement technology works by collecting and amplifying the light that’s already present, even when it’s too faint for human eyes to detect. On the darkest nights, tiny amounts of light from stars, distant sources, or even infrared light can still be found. Night vision goggles with image enhancement technology gather all this available light and amplify it thousands of times. This produces a bright, clear image that allows users to see their surroundings in the dark.
The detailed working mechanism is as follows:
- Infrared Radiation Detection: Infrared night vision apparatuses employ infrared photoelectric conversion elements, such as photodiodes or photomultiplier tubes, to detect the infrared radiation emitted within the ambient environment. In nocturnal or low-light settings, a multitude of objects emit infrared radiation, which, to a certain degree, can permeate through fog, smoke, and conditions of extremely diminished visibility.

- Signal Amplification and Processing: The infrared photoelectric conversion components transform the detected feeble infrared radiation into faint electrical signals, which are subsequently amplified via amplification circuits. These amplified signals are then relayed to the image processing segment.

- Image Enhancement: The image processing module undertakes the tasks of filtering, amplifying, and modifying the weak electrical signals with the aim of augmenting the contrast and sharpness of the image. This entails applying gain to the image and meticulously adjusting parameters like brightness, contrast, and saturation.

- Image Display: The signals that have been subjected to the enhancement process are transmitted to display devices, such as liquid crystal screens or viewing glasses. The resultant displayed images are capable of furnishing more distinct and identifiable target information. It should be noted that the scene visualized via infrared radiation may deviate from that perceptible by the human eye, as infrared radiation is emitted in accordance with the heat of objects and is not constrained by visible light.
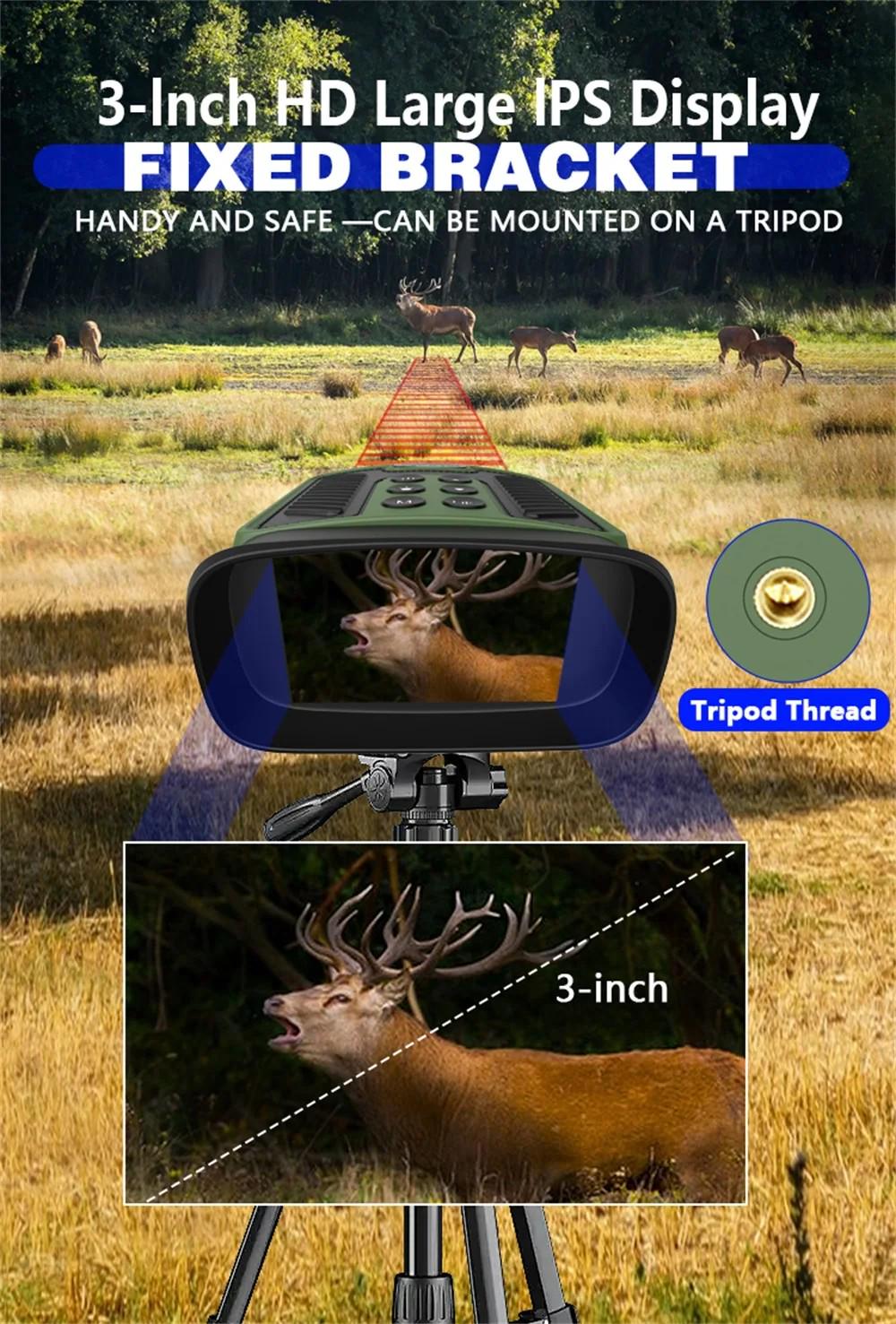
In addition, with the help of infrared lights, such as infrared flashlights, you can see further away.

Thermal Imaging
The second type of night vision technology, thermal imaging, is all about heat. Objects that generate heat, such as animals, people, and even vehicles, emit infrared light. Thermal imaging goggles detect this infrared light and convert it into an image based on the temperature differences between objects. The result is a detailed picture where warmer objects appear brighter or stand out against cooler backgrounds.
Thermal imaging is particularly useful for detecting living creatures, making it an excellent tool for search-and-rescue operations or wildlife observation. It also works well in the darkest conditions where there’s little to no visible light to enhance.
Common Uses of Night Vision Goggles
Night vision technology is widely used by the military and law enforcement for tasks like navigation, surveillance, and locating people in the dark. Beyond these professional uses, night vision goggles have become popular for activities like hunting, camping, and observing nocturnal wildlife. Although this article discusses night vision devices. But both infrared night vision devices and thermal imaging can be used during the day.
Have you ever wondered why night vision images often appear green? This isn’t just a random choice. Human eyes are especially sensitive to green light, and looking at green images for extended periods is more comfortable than other colors. That’s why night vision goggles are designed to display images in shades of green.
Could You Use Night Vision Goggles?
While night vision goggles are often associated with spies, soldiers, and police officers, they’re also accessible to everyday people. Whether you’re exploring nature after dark, searching for wildlife, or even playing nighttime sports, night vision goggles could be a fun and practical tool.
Have you ever experienced the thrill of seeing in the dark? Night vision goggles make the invisible visible, opening up a world of possibilities for adventures after sunset. Who knows? Maybe one day you’ll get to try a pair and see the night in a whole new light!






